Meshing Services
Meshing is a critical step in Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) analysis, especially for crash and impact testing. It involves creating a mesh, which is a collection of elements that approximates the geometry of the physical system being analyzed. Here’s why meshing is so important:
Meshing capabilities:
- Sheet metal and Plastic Parts
- Body-in-White (BIW): Structural components such as chassis, frame, and body structures.
- Bumpers: Front and rear bumpers
- Energy Absorbers
- Side Door Panels
- Roof and Pillars
- Suspension Components
- Seating Systems Restraint
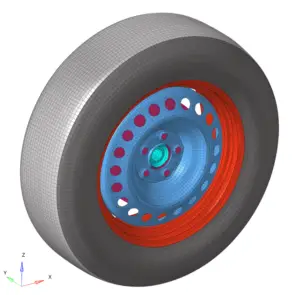
- Wheels and Tires
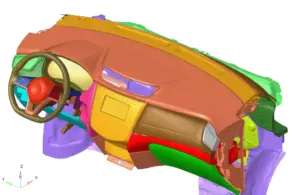
- Interior Components: Meshing of dashboard, trim, and other interior
- components
- Full Vehicle Crash with Dummies: for crash simulations and safety assessments.
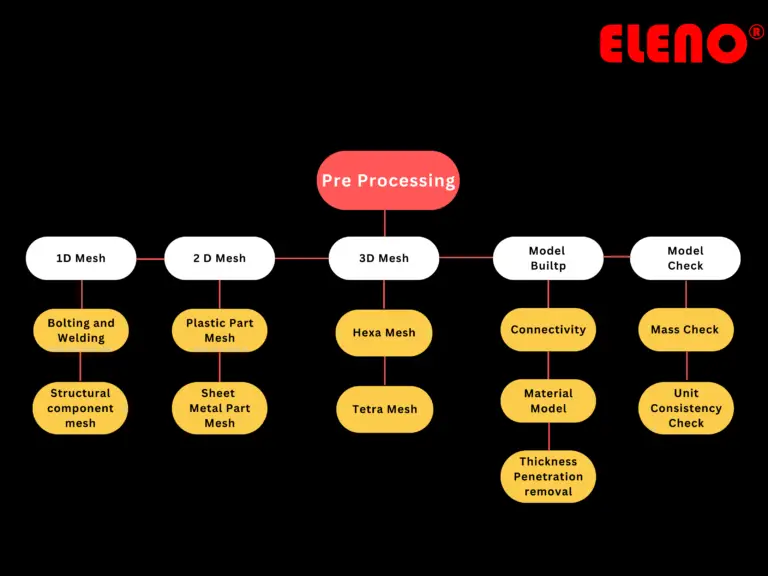
Accuracy of Results
Meshing converts a continuous domain into a discrete one, allowing for the numerical solution of physical phenomena. The quality of the mesh directly affects the accuracy of the CAE analysis. A well-defined mesh can capture the behavior of the system under crash and impact conditions more accurately.
Efficiency
A good mesh helps in reducing the computational resources required for the simulation. By optimizing the number of elements, the analysis can be run more efficiently without compromising the results’ accuracy.
Material Behavior
During crash and impact testing, understanding how different materials respond is crucial. Meshing allows for the detailed modeling of material properties, which is essential for predicting how materials will behave under stress.
Structural Integrity
Meshing helps in assessing the structural integrity of components by allowing for the detailed analysis of stress distribution and deformation during impact.
Safety Standards
For automotive vehicles, for instance, meshing is used to ensure that designs meet safety standards. It helps in simulating various crash scenarios and evaluating the vehicle’s crashworthiness¹.
Design Optimization
Meshing is also used in multi-disciplinary design optimization (MDO), where it helps in reconciling different design requirements for durability, NVH (Noise, Vibration, and Harshness), and crash performance within a common framework¹.